In the ever-evolving landscape of financial reporting and regulatory compliance, auditors play a critical role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial information. To navigate this complex world effectively, auditors must possess a firm grasp of key concepts that underpin their profession. "Key Concepts Every Auditor Should Know" is the definitive guide to empowering auditors with the foundational knowledge they need to excel in their field.
Chapter 1: Auditing Standards and Frameworks
This chapter provides an in-depth examination of the International Standards on Auditing (ISAs) and other relevant frameworks that govern auditing practices. Auditors will gain a clear understanding of the fundamental principles of auditing, including risk assessment, materiality, and reporting responsibilities.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 1340 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 238 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Alt text: 
Chapter 2: Financial Reporting and Internal Controls
Auditors must have a thorough knowledge of financial reporting frameworks such as IFRS and US GAAP. This chapter delves into the concepts of financial reporting and the role of internal controls in ensuring the reliability of financial statements.
Alt text: 
Chapter 3: Risk Assessment and Audit Planning
Effective auditing requires a systematic approach to risk assessment and audit planning. This chapter guides auditors through the process of identifying, assessing, and responding to audit risks, ensuring a tailored and efficient approach to their engagements.
Alt text: 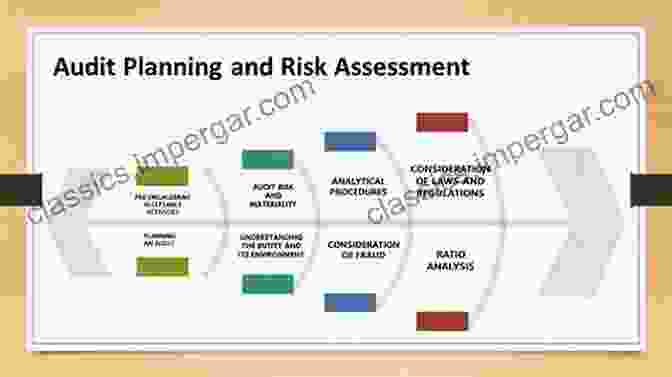
Chapter 4: Sampling and Analytical Procedures
Auditors rely on sampling and analytical procedures to obtain evidence and draw s about the financial statements. This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of these techniques, empowering auditors to effectively evaluate audit evidence and make informed judgments.
Alt text: 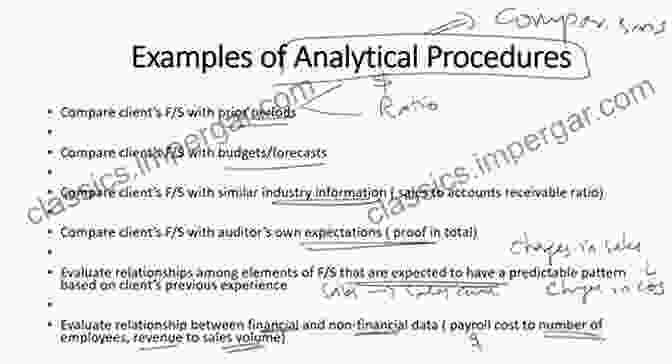
Chapter 5: Audit Evidence and Working Papers
Audit evidence is the cornerstone of the auditor's opinion. This chapter explores the different types of audit evidence, the criteria for evaluating its sufficiency and reliability, and the importance of proper documentation in audit working papers.
Alt text: 
Chapter 6: Reporting and Communication
The auditor's report is the culmination of the audit process. This chapter provides guidance on the preparation and issuance of audit reports, including the different types of opinions and the communication of audit findings to management and other stakeholders.
Alt text: 
Chapter 7: Ethical Considerations and Professional Standards
Auditors are bound by strict ethical considerations and professional standards. This chapter explores the importance of professional skepticism, independence, and confidentiality, and provides a framework for ethical decision-making in the auditing profession.
Alt text: 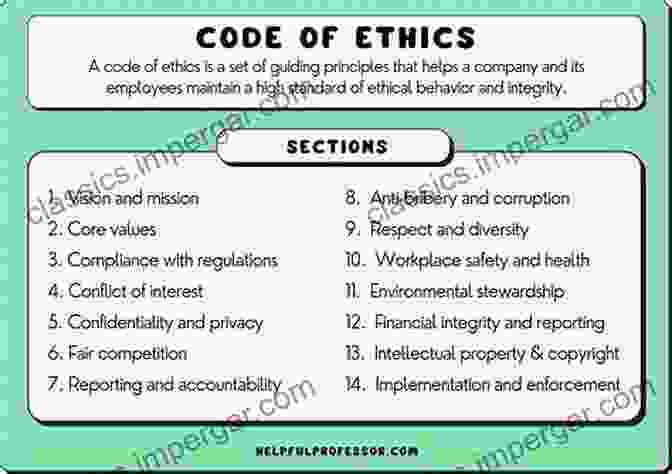
Chapter 8: Emerging Issues and Future Trends
The auditing profession is constantly evolving in response to emerging issues and technological advancements. This chapter provides insights into key trends and challenges facing auditors, such as data analytics, artificial intelligence, and sustainability reporting.
Alt text: 
"Key Concepts Every Auditor Should Know" is an indispensable resource for both aspiring and experienced auditors. By mastering the concepts outlined in this book, auditors will gain the confidence and competence to navigate the complexities of the auditing profession. This comprehensive guide will empower them to meet the challenges of the future and contribute to the integrity and reliability of financial reporting.