5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4835 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 298 pages |
Prepare yourself for a captivating exploration into the annals of European history. This book delves into the intricate web of events known as the European Restorations, an era that redefined the political, social, and economic landscape of the continent following the tumultuous reign of Napoleon Bonaparte.
The Legacy of Napoleon
The Restoration Era began in the wake of Napoleon's defeat at Waterloo in 1815. Bonaparte's conquests and reforms had left an indelible mark on Europe, challenging traditional monarchies and fostering a spirit of nationalism. The task of restoring stability and Free Download fell upon the shoulders of conservative statesmen determined to return Europe to its pre-revolutionary status quo.
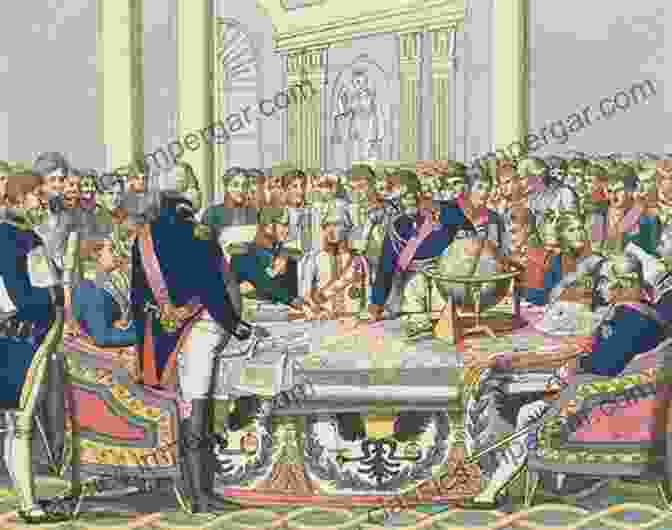
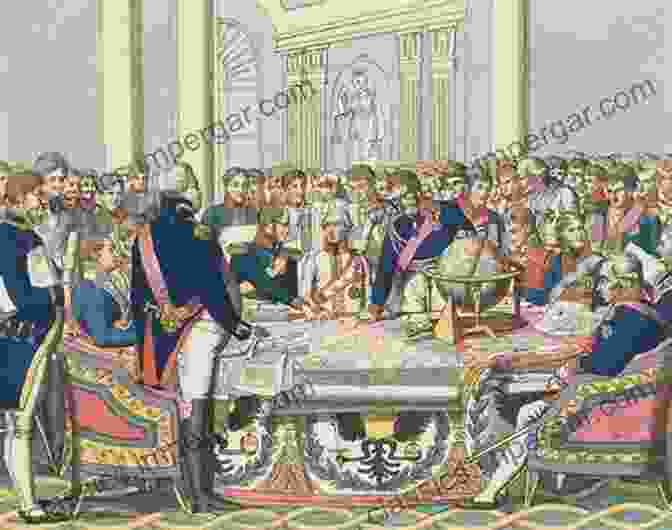
The Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna, convened in 1814-15, played a central role in shaping the post-Napoleonic Free Download. Guided by the principles of legitimacy and balance of power, the delegates sought to redraw the political map of Europe, returning territories to their former rulers. The Congress also established the Concert of Europe, an alliance system designed to maintain peace and prevent future conflicts.

Political and Social Reforms
The Restoration Era was characterized by a diverse range of political and social reforms. In some countries, constitutional monarchies emerged, introducing elements of parliamentary government and civil liberties. In others, absolute monarchies were restored, leading to periods of repression and political instability.
Social reforms varied widely, with some nations embracing industrialization and urbanization, while others clung to feudal traditions and rural lifestyles. The Industrial Revolution gained momentum in Britain and parts of Western Europe, transforming economic and social structures.
Economic Consequences
The Napoleonic Wars had devastated the European economy, leaving behind war debts, currency fluctuations, and disruptions to trade. The Restoration period witnessed efforts to stabilize economies, including the establishment of central banks, the adoption of standardized currencies, and the development of new industries.
However, economic recovery varied significantly across Europe. Some countries, particularly Britain, benefited from industrialization and trade, while others faced prolonged economic stagnation and social unrest.
Intellectual and Cultural Movements
The Restoration Era was also a time of great intellectual and cultural ferment. Romanticism, a literary and artistic movement that emphasized emotion, imagination, and the individual, flourished. This period saw the rise of notable writers, poets, and artists, including Byron, Shelley, and Goya.

Challenges and Legacies
The European Restorations faced ongoing challenges and tensions. Liberal and nationalist movements emerged, demanding greater political participation and self-determination. Revolutions erupted in various parts of Europe, leading to periods of upheaval and instability.
Despite these challenges, the European Restorations left a lasting legacy. It preserved the balance of power in Europe for decades, preventing major conflicts until the outbreak of World War I. The era also laid the foundation for modernization and industrialization, shaping the course of European history for centuries to come.
The History of the European Restorations is an essential read for anyone seeking to understand this pivotal era. It offers a comprehensive insight into the political, social, economic, and cultural transformations that shaped Europe in the 19th century.
Through meticulous research and vivid storytelling, this book transports readers back in time, immersing them in the complexities of a world in flux. It is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of human societies, and a valuable contribution to the study of European history.